
Connecting MongoDB with Prisma ORM
As a non-relational database, MongoDB has also begun to gain prominence in today's internet world. However, using MongoDB within a Node.js project differs from using relational databases like PostgreSQL.
It's quite inconvenient to have to delve into the specifics of different ORMs each time you switch databases. Sometimes, you even have to master the calling methods of two to three different database interfaces.
Hence, there is an urgent need for a suitable ORM tool that allows us to easily switch between PostgreSQL and MongoDB.
Now, I'm recommending to you a new type of ORM tool - Prisma. While there are many ORM tools available on the market, Prisma is the only one I've come across. It seems to be quite user-friendly, so let's give it a try.
Actually, the specific steps provided by the official documentation are very detailed, so I have nothing more to add. Just follow the instructions once. Below is a summary of some steps. There may be differences due to version changes, but the basics are generally the same.
Install the Prisma CLI globally on your system using npm, yarn, or pnpm:
npx prismaUse prisma init to create a new Prisma project, then a new directory called prisma that contains a file called schema.prisma will appear.
Configure the Prisma Client to connect to your MongoDB database by providing the connection URL and necessary authentication credentials.
datasource db {
provider = "mongodb"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}In this case, the url is set via an environment variable which is defined in .env (the example uses a MongoDB Atlas URL):
DATABASE_URL="mongodb+srv://test:test@cluster0.ns1yp.mongodb.net/myFirstDatabase"Define your data model in schema.prisma using the Prisma Schema Language to specify the structure of your database schema
datasource db {
provider = "mongodb"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client-js"
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
slug String @unique
title String
body String
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
email String @unique
name String?
address Address?
posts Post[]
}After generating the Prisma Client using prisma generate, Prisma will automatically create your custom objects
With prisma db push, prisma will adjust your database tables using the provided database URL, creating new tables without deleting unnecessary ones. Additionally, Prisma will run prisma generate automatically after executing this command. If you wish to skip generation, you can use prisma db push --skip-generate.
When connecting to MongoDB using Prisma, it's essential to pay close attention to several potential pitfalls. Therefore, when composing the URL for the database connection, please carefully consider the following points:
First, let's examine the basic format of the database connection URL, referring to the official instructions.
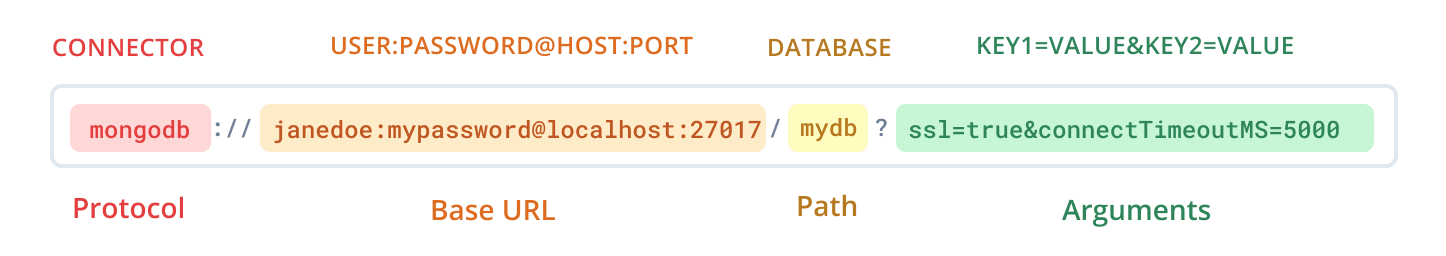
The URL consists of several basic components: protocol, credentials, host, database, and parameters. In simple terms, it should resemble the following structure:
mongodb://USERNAME:PASSWORD@HOST/DATABASEPlease ensure the URL adheres to this format.
-
Ensure Correct Username and Password
This point is straightforward. Make sure you enter the correct username and password.
-
Avoid Misleading Characters
Certain characters can mislead parsing, such as
@,-,:, and others. Refer to the link for special character handling. You need to encode special characters as percent-encoded values to ensure the URL is correct. Refer to MDN's encoding guide for encoding methods.This point may seem less important at first glance, but it's easy to overlook. If your connection URL consistently prompts errors, you should double-check to see if this is the issue.
-
Ensure Database Name is Provided
It's quite peculiar, but Prisma requires you to provide a database name. Otherwise, it will resort to its default behavior, which is:
Name of the database to use. If none is specified but the authSource option is set then the authSource database name is used.
If neither the database in the connection string nor the authSource option is specified then it defaults to admin.
Please note, at the end of the database name, do not include the
/symbol. Otherwise, it won't be parsed correctly. This point is crucial, as it's where Prisma can be quite tricky. -
Ensure Your Hostname is Normal
Ensure that the domain name following the username and password is normal. Actually, making a domain name abnormal is quite challenging. However, being predisposed to encountering various issues due to my "buggy" nature, I've experienced all sorts of problems😭.
Avoid including strange characters in the HOST section. This point is somewhat similar to the second point. However, my hostname was
@cluster-test.sdauxzc.mongodb.netand that single
-almost cost me dearly. While it can be opened normally in MongoDB Compass, Prisma does not parse it correctly, rendering the host inaccessible. This is something to be aware of.